
DNA is the basis for the diversity of living things. Energy change is required as atoms rearrange in chemical processes. Energy is conserved, and its transformation can affect living things and the environment. The formation of the universe can be explained by the big bang theory.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt

Atoms and molecules are building blocks of matter. Organic chemistry and its applications have significant implications for human health, society, and the environment. The mole is a quantity used to make atoms and molecules measurable. Matter and energy are conserved in chemical reactions. Solubility within a solution is determined by the nature of the solute and the solvent.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt
Earth materials are changed as they cycle through the geosphere and are used as resources, with economic and environmental implications. Plate tectonic theory explains the consequences of tectonic plate interactions. The transfer of energy through the atmosphere creates weather, and this transfer is affected by climate change. The distribution of water has a major influence on weather and climate. Astronomy seeks to explain the origin and interactions of Earth and its solar system.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt

Life is a result of interactions at the molecular and cellular levels. Evolution occurs at the population level. Organisms are grouped based on common characteristics.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt

Physics 11 explores how to use Newton's laws and energy to predict motion or explain why objects move the way they do. Learners should have a strong understanding of Math 10, and an understanding of precalculus 11 is an asset.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt

Why do people have different personalities? What is intelligence and how its it measured? Why is one person attracted to another; and why do people dream?
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt

Scientific processes and knowledge inform our decisions and impact our daily lives. Scientific knowledge can be used to develop procedures, techniques, and technologies that have implications for places of employment. Scientific understanding enables humans to respond and adapt to changes locally and globally.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt
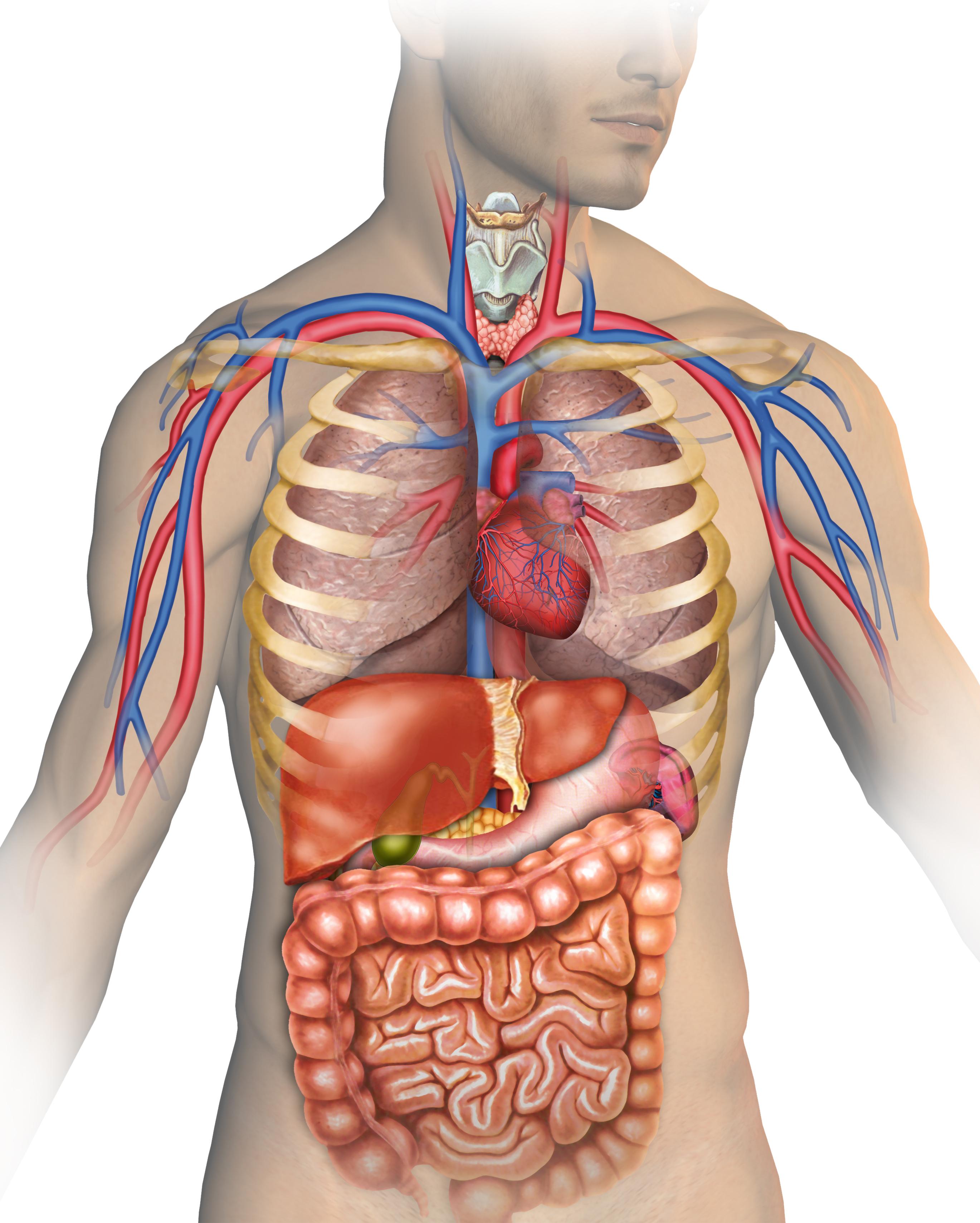
Homeostasis is maintained through physiological processes. Gene expression, through protein synthesis, is an interaction between genes and the environment. Organ systems have complex interrelationships to maintain homeostasis.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt
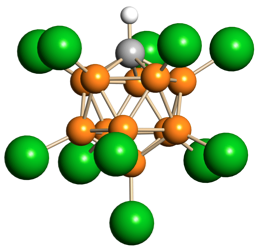
Reactants must collide to react, and the reaction rate is dependent on the surrounding conditions. Dynamic equilibrium can be shifted by changes to the surrounding conditions. Saturated solutions are systems in equilibrium. Acid or base strength depends on the degree of ion dissociation. Oxidation and reduction are complementary processes that involve the gain or loss of electrons.
- Teacher: Cory Vaillancourt

Physics 12 generalizes Newton's laws to rotation (torque) and planetary motion, introduces conservation of momentum, then introduces electromagnetism. Students are assumed to have a strong understanding of physics 11 and precalculus 11.
- Teacher: Ron McLeod